Before you start investing, it’s essential to understand a company’s profit structure. Businesses operate on revenue, but not all revenue is profit. Understanding the concepts of Gross Profit, Operating Profit, and Net Income will help investors assess a company’s true profitability and financial health.
Profit & Loss Statement Visualized
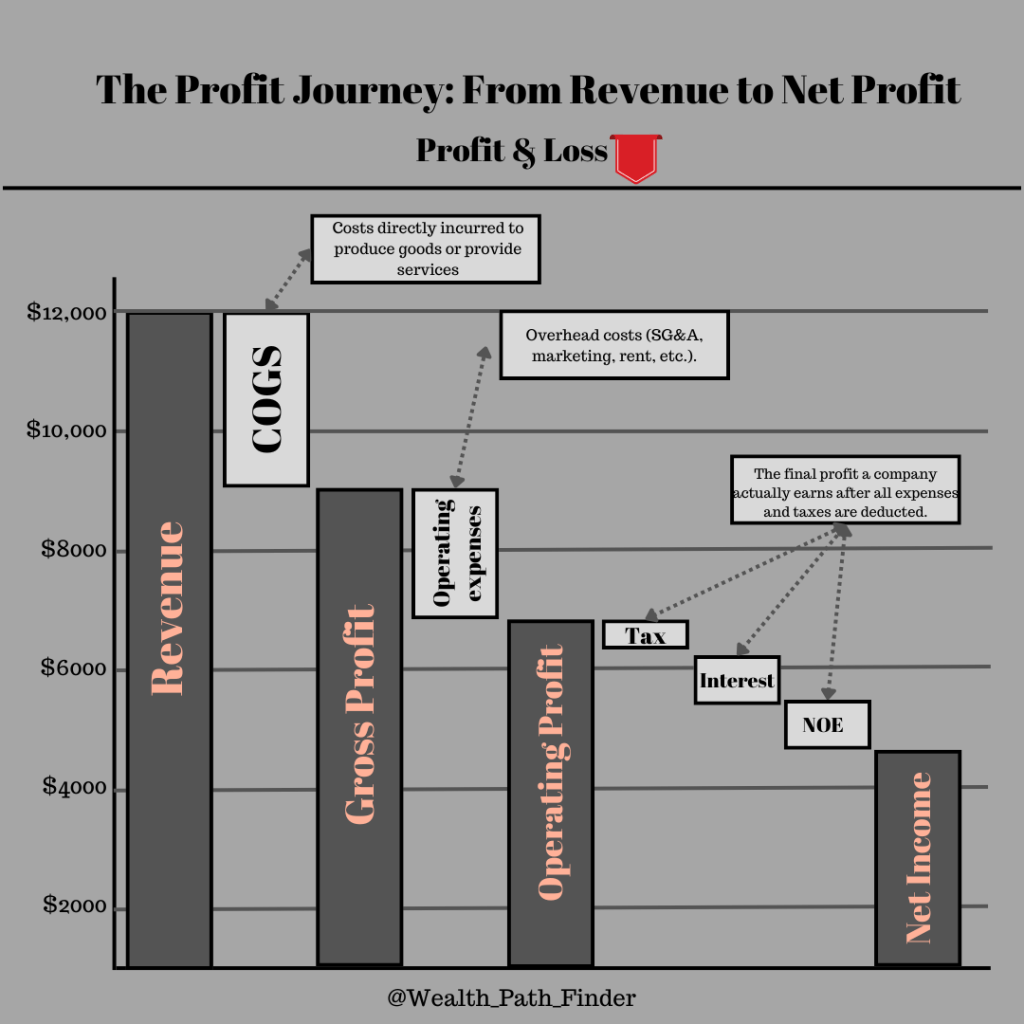
Revenue
Definition: The total revenue a company earns from selling products or providing services.
Use: Used to evaluate a company’s market share and revenue growth. Increasing revenue indicates success in the market and potential for growth.
COGS (Cost of Goods Sold)
Definition: Costs directly incurred to produce a product or provide a service.
Examples: material costs, labor costs.
Utilization: Low COGS means efficient production, which leads to higher Gross Profit.
Gross Profit
Definition: Revenue – COGS
Shows how profitable a company’s core operating activities are.
Use: To assess how profitable a company’s products and services are.
A high gross profit margin indicates good product pricing and production efficiency.
Operating Expenses
Definition: The overhead costs of a company’s day-to-day operational activities.
Examples: Rent, marketing expenses, research and development expenses.
Use: An important metric for optimizing Operating Profit through cost management.
Operating Profit
Definition: Gross Profit – Operating Expenses
The net income generated by a company’s operating activities alone.
Use: A key metric for measuring the profitability of a business, important for assessing the sustainability of a company.
Tax, Interest, Non-Operating Expenses
Tax: Corporate taxes that a company pays to the government.
Interest: The cost the company owes on a loan or debt.
Non-Operating Expenses: Expenses outside of operating activities, for example, losses on investments, losses on disposal of assets, etc.
Net Income
Definition: Operating Profit – (Tax + Interest + Non-Operating Expenses)
The bottom line profit that a company actually makes after deducting all expenses.
Use: Important for calculating earnings per share (EPS), evaluating dividend potential, and determining company value tied to stock price.
Understanding the journey from revenue to net income is essential for making informed investment decisions. Each step reveals critical insights about a company’s profitability, efficiency, and overall financial health. By mastering these concepts, you’ll be better equipped to analyze businesses and identify strong investment opportunities.
If you found this helpful, please like and share! Have questions? Drop a comment below! For more quick and simple financial insights, follow @Wealth_Path_Finder on Instagram.
Leave a comment