From traditional choices like stocks, bonds, and real estate to modern innovations like cryptocurrency and exchange-traded funds, each type of investment offers unique benefits and risks. Understanding these options is key to making informed decisions that align with your financial goals. In this post, we’ll provide a clear and concise overview of the major types of investments, helping you navigate the world of investing with confidence and purpose.
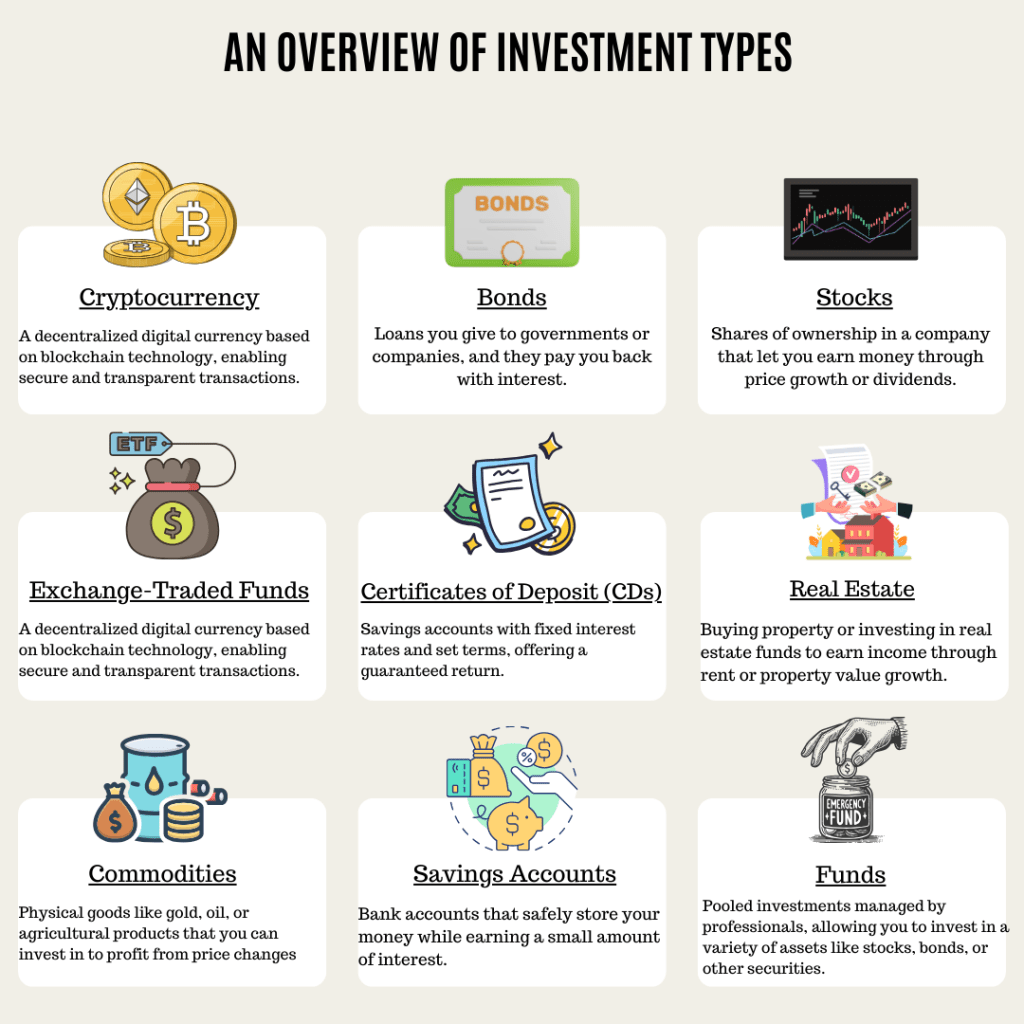
The image above highlights key investment types, each with unique benefits and risks. Let’s dive deeper to explore how they work and help you grow your wealth.

Cryptocurrency: a digital or virtual currency that uses blockchain technology for secure, decentralized, and transparent transactions.
Benefits
High Return Potential: Cryptocurrencies have shown the ability to deliver substantial returns over a short period, making them attractive for high-risk investors.
Global Accessibility: Cryptocurrencies can be traded 24/7, providing flexibility and access to global markets.
Risks
Extreme Volatility: Prices can swing wildly, leading to significant losses if the market moves against your position
Lack of Regulation: Limited oversight increases risks of fraud, scams, or market manipulation.

Bond: A bond is a fixed-income investment where investors lend money to entities (like governments or corporations) in exchange for regular interest payments and the return of principal at maturity.
Benefits
Stable Income: Provides predictable interest payments, making it a reliable source of income.
Lower Risk: Generally less volatile than stocks, offering more stability.
Risks
Credit Risk: Risk of default if the issuer is unable to meet payment obligations.
Inflation Risk: Fixed payments may lose purchasing power during periods of high inflation.

Stocks: represents a share of ownership in a company, giving investors a claim on the company’s assets and earnings
Benefits
High Growth Potential: Historically, stocks have offered higher returns compared to other asset classes over the long term.
Liquidity: Stocks are easy to buy and sell on public exchanges, providing quick access to cash if needed.
Risks
No Guaranteed Returns: Unlike bonds, there is no fixed income, and investments can result in a loss of capital.
Market Volatility: Stock prices can fluctuate significantly due to market conditions or company performance.

ETF(Exchange Trading Fund): a collection of securities, such as stocks or bonds, that is traded on an exchange like a stock, offering diversification and flexibility.
Benefits
Low Costs: Typically has lower fees compared to mutual funds, making them cost-effective.
Liquidity and Flexibility: Traded like stocks, ETFs allow buying and selling throughout the trading day at market prices.
Risks
Market Risk: ETF values can fluctuate with the underlying assets, exposing investors to potential losses.
Liquidity Risk: Some niche or low-volume ETFs may have wider bid-ask spreads, making trading less efficient.

Certificate of Deposit (CD): a time deposit offered by banks and credit unions, where investors lock in a fixed amount of money for a set period in exchange for guaranteed interest payments.
Benefits
Guaranteed Returns: Offers fixed interest rates, providing a predictable and secure return on investment.
Low Risk: Insured by the FDIC or NCUA (up to applicable limits), making them one of the safest investment options.
Risks
Lack of Liquidity: Funds are locked in until maturity, and early withdrawals may incur penalties.
Inflation Risk: Fixed interest rates may not keep up with inflation, reducing purchasing power over time.

Real Estate: investing involves purchasing property to generate income through rental payments, appreciation in value, or both.
Benefits
Steady Income: Rental properties provide a consistent cash flow through monthly rent.
Appreciation Potential: Real estate typically increases in value over time, offering long-term capital gains.
Risks
High Initial Costs: Requires significant capital for down payments, maintenance, and other expenses
.Market and Location Dependency: Property values can be heavily influenced by local market conditions and economic factors.

Commodities: are physical goods like gold, oil, agricultural products, or natural resources that can be traded on exchanges and used as investment assets.
Benefits
Diversification: Provides exposure to a unique asset class, reducing overall portfolio risk.
Global Demand: Commodities are essential for industries, ensuring consistent demand over time.
Risks
No Income Generation: Unlike stocks or bonds, commodities don’t provide dividends or interest
.Complexity: Requires specialized knowledge to understand market trends and factors influencing prices.

Saving Account: a deposit account offered by banks or credit unions that allows individuals to earn interest on their money while maintaining easy access to funds.
Benefits
Safety: Deposits are insured by the FDIC or NCUA (up to applicable limits), ensuring your money is protected.
Predictable Growth: Earns interest over time, providing a secure way to grow savings without risk.
Risks
Opportunity Cost: Money in a savings account could potentially earn higher returns in other investments.
Low Returns: Interest rates are typically lower than inflation, meaning your purchasing power may decline.

fund: is a pooled investment vehicle where money from multiple investors is combined and managed by professionals to invest in assets like stocks, bonds, or other securities.
Benefits
Professional Management: Managed by experienced professionals who make investment decisions on your behalf.
Diversification: Provides exposure to a wide range of assets, reducing risk through portfolio diversification.
Risks
Market Dependency: Performance is tied to the underlying assets, meaning market downturns can result in losses.
Lack of Control: Investors have no say in the specific assets chosen within the fund.
Investing is a powerful tool to grow your wealth, but each option comes with unique benefits and risks. Diversify your portfolio, align investments with your goals, and stay informed to make smarter financial decisions. With the right strategy, you can build a secure and successful financial future.
For more tips and insights, follow us on Instagram at @Wealth_Path_Finder! If you enjoyed this post, don’t forget to like and share it with others. Thank you for reading!
Leave a comment